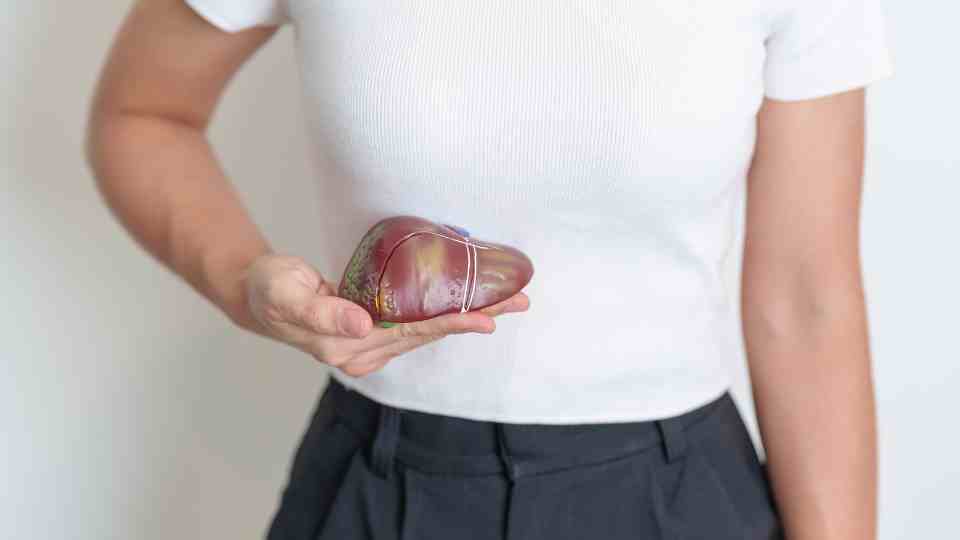
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that targets the liver and spreads through contact with the blood or bodily fluids of an infected person. It is a global health issue, with the highest prevalence rates found in parts of East Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa. Moderate rates of infection are reported in the Amazon, Southern and Eastern Europe, the Middle East, and the Indian subcontinent, while Western Europe and North America experience relatively low rates. Although the risk to travellers is generally low, certain activities such as unprotected sex, medical procedures using contaminated equipment, or engaging in contact sports in high-prevalence areas can significantly increase the likelihood of exposure. Travellers staying for long durations or working in healthcare settings are also at heightened risk.

Symptoms
Hepatitis B often presents without symptoms, particularly in children, while adults are more likely to experience noticeable signs. When symptoms occur, they may include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), fever, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite. Acute infections can lead to persistent hepatitis B in 80–90% of infants infected in the first year of life, compared to only 5% in adults. Chronic hepatitis B infections can result in serious complications such as liver failure, cirrhosis, or liver cancer. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for preventing these severe outcomes, particularly in individuals with long-term infections.

Vaccination
The hepatitis B vaccine is a highly effective preventative measure, recommended for individuals at risk of exposure, including travellers to high-prevalence regions. Vaccination involves a series of three injections over flexible timeframes, depending on how urgently protection is needed.
For those asking how long does the hepatitis B vaccine last, Public Health England states that a booster dose is not generally required for travellers unless they are at ongoing risk. Immunity is typically long-lasting after completing the vaccine series. Blood tests to confirm immunity are only advised for specific groups, such as healthcare workers and individuals with kidney failure, to ensure adequate protection. The vaccine also helps prevent the transmission of other bloodborne viruses like HIV and hepatitis C, making it an essential part of travel health preparations.
Book Now
Book your appointment with us today to receive your vaccine and other essential travel vaccinations. Let us help you travel with confidence and peace of mind.